Elevators
USE:
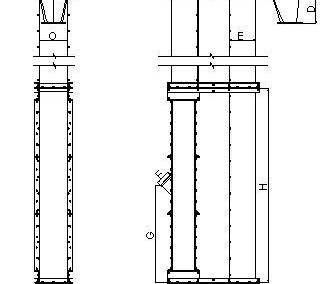
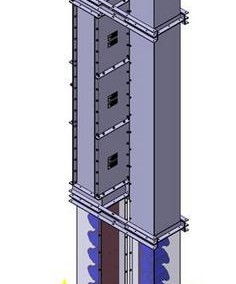
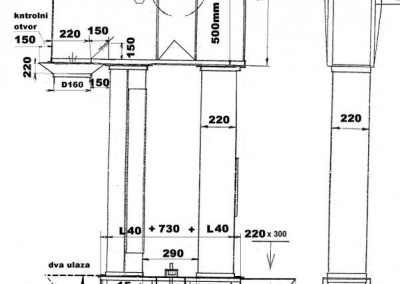
Elevators are used for vertical grain transport in silos. Parts of the elevator are: head section, boot section, pipes, belt with buckets.
HOW IT WORKS:
- Grain is brought to elevator through an opening in the boot section that can be set in front or back side of the elevator.
- Buckets grab grain and carry it up.
- Due to centrifugal force that acts on the curve of a drum, grain flies out of the bucket and moves along trajectory which represents the resultant of volume of drum speed and gravitational acceleration.
- Drum speed volume and head profile should be selected in a way that each grain falls into outlet orifice on the head of elevator.
Elevator Capacity (Q) is calculated according to the formula:
Q= Z x i x v x u x k(kg/h)
Z= number of buckets
i= volume of bucket (m3)
v= band velocity (m/sec)
u= bulk density (kg/m3)
k= coefficient of elevator loading
Engine power of the elevator (N) is calculated according to the formula:
N= (Q x H) : (367 x k) (Kw)
Q= elevator capacity (kg/s)
H= lifting height (m)
k= coefficient of efficiency of elevator.
Switches and pipelines for grain transport
USAGE AND OPERATION:
- Pipelines are used for grain gravitational transport.
- Projected diameter of a pipeline is D= 200mm.
- Wall thickness of pipeline is 2mm.
- During grain transport through pipeline, special attention needs to be brought to the angles under which pipeline is installed.
- If the angle is more vertical, grain fall buffers are necessary.
- Grain that falls vertically heats the pipeline and shortens its service life.
- Soy transport through pipeline uses up pipe walls the most. In this case pipelines need to be replaced more frequently.
- Switches, routers serve to direct grain in a certain direction.
- Switchers are designed for manual switching.
- Switchers can be controlled by cables from ground.